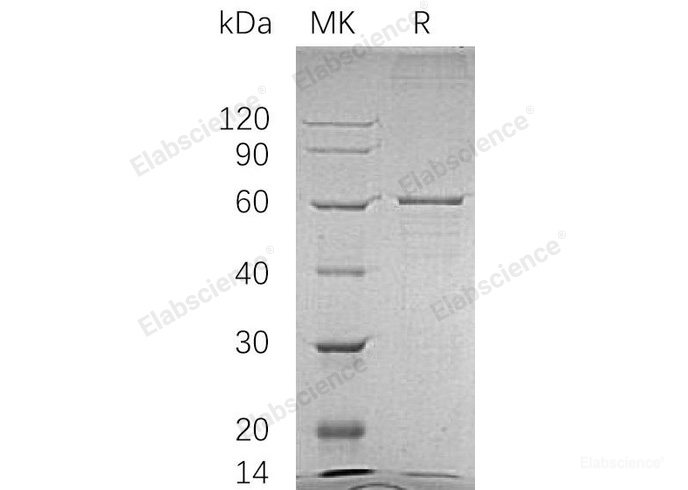
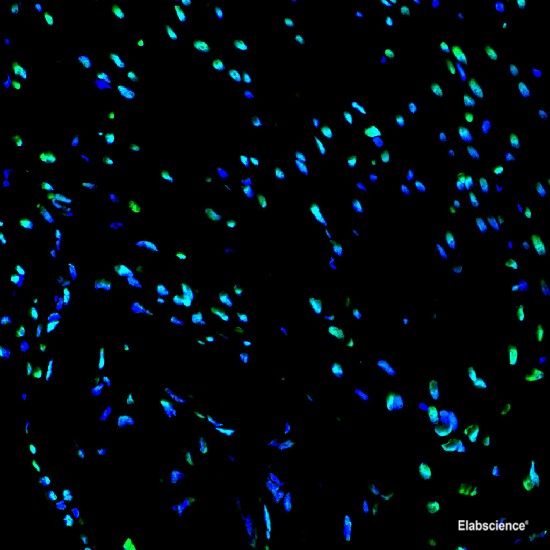
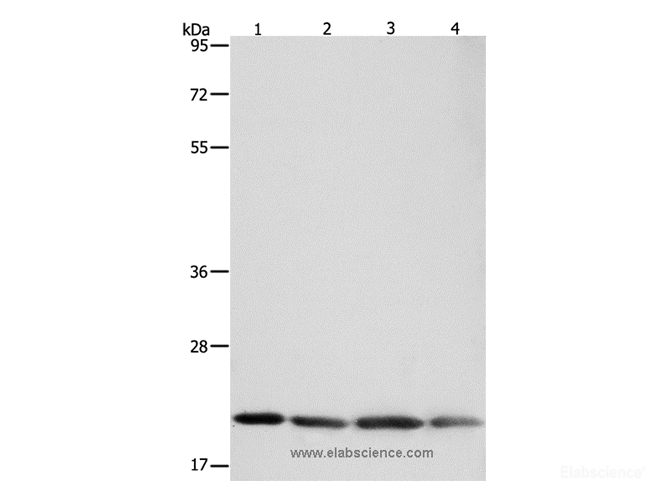
Background
Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk, also known as B lymphocyte kinase, p55-Blk and BLK, is a member of theprotein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family and SRC subfamily. BLK / p55-Blk is expressed in lymphatic organs, pancreatic islets, Leydig cells, striate ducts of salivary glands and hair follicles. BLK / p55-Blk is a src-family protein tyrosine kinase specifically expressed in B-lineage cells of mice. The early onset of Blk expression during B-cell development in the bone marrow and the high expression levels of Blk in mature B cells suggest a possible important role of Blk in B-cell physiology. It is a modulator of beta-cells function, acting through the up-regulation of PDX1 and NKX6-1 and consequent stimulation of insulin secretion in response to glucose. Defects in BLK are a cause of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 11 which is a form of diabetes that is characterized by an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance, onset in childhood or early adulthood (usually before 25 years of age), a primary defect in insulin secretion and frequent insulin-independence at the beginning of the disease.