Cell Function
Precautions for Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
Source: Elabscience®Published: Jan 16,2024
Annexin V is one of the commonly used methods for detecting early cell apoptosis. Although the experimental operation is not difficult, obtaining a beautiful Flow Cytometry result is not easy, and any negligence in detail can lead to unsatisfactory experimental results. This article introduces the precautions during the Annexin V experiment and the experimental details that cannot be ignored.
01. Detection Principle of Annexin V Assay
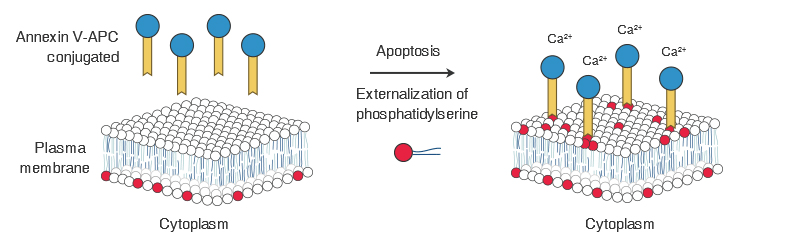
Annexin V is a Ca2+dependent phospholipid binding protein with a molecular weight of 35-36kD, which can specifically bind to phosphatidylserine (PS) with high affinity. During the early stage of apoptosis, the loss of cell membrane asymmetry will take place in which embedded
phosphatidylserine (PS) residues in the plasma membrane become externalized. Using Annexin V labeled with fluorescence as a fluorescent probe, combined with nucleic acid dyes such as PI, 7-AAD, DAPI, etc., can accurately distinguish between normal cells, early apoptotic cells, and late apoptotic cells.
02. Display of Annexin V results
01. Experimental precautions
a. Precautions for sample preparation
1) Adhering cells should be digested using pancreatic enzymes that do not contain EDTA as much as possible. If it is necessary to use pancreatic enzymes containing EDTA, after digestion is terminated, the cells should be washed clean and EDTA should be removed as much as possible.
2) Cells, tissues, and other samples that are difficult to be digested can be digested in batches to avoid over digestion of previously digested cells, which can lead to false positive results.
3) Mechanical force can damage cells, and any violent behavior during operation can increase the percentage of apoptosis in the cells themselves. To achieve good experimental results, try to minimize cell damage
b. Precautions for experimental design
The control setting in the Flow Cytometry experiment has always been frustrating, so how the control should be set in the Annexin V experiment? What is the role of each control? The following table is for your reference:
Table 1. Control setting of Annexin V Flow Cytometry apoptosis experiment
|
Group |
Annexin V |
Nuclear dye |
Sample |
Purpose |
|
Blank control |
- |
- |
Cells without any treatment |
Determine instrument threshold and adjust cell position |
|
Biological control |
+ |
+ |
Cells without any treatment |
Exclude the impact of operations on experimental results, assist in gating, and determine if the treatment is effective |
|
Single positive control 1 |
+ |
- |
Cells with obvious apoptosis |
Adjusting compensation and channel voltage |
|
Single positive control 2 |
- |
+ |
Cells with obvious apoptosis |
Adjusting compensation and channel voltage |
Notes:
1) The single positive control group must use cells with confirmed apoptosis, as adjusting compensation requires sufficient positive signals.
2)If the cells show spontaneous fluorescence, blank control and single positive control need to use cells without spontaneous fluorescence, and an additional tube of cells with fluorescence but without any dye needs to be added as a single positive control.
-
If cells with green fluorescence, such as GFP, the appropriate kit can be selected based on the configuration of
the Flow Cytometer:
a) If the Flow Cytometer has a DAPI channel, choose the Annexin V-APC/DAPI Apoptosis Kit (E-CK-A258).b) If the Flow Cytometer does not have a DAPI channel, choose the Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Apoptosis Kit (E-CK-A218).
- If cells with red fluorescence, such as mcherry/RFP, choose the Annexin V-APC/DAPI Apoptosis Kit (E-CK-A258).
c. Precautions for data analysis
To obtain good experimental results, data analysis is also a crucial step. How should data analysis be done? In summary, it includes instrument settings, adjustment compensation, and gate settings.
1)Instrument settings: The instrument settings mainly include two aspects: threshold and voltage of each channel. The threshold needs to be reasonable and cannot be too large or too small.
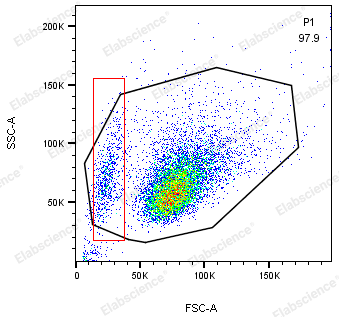
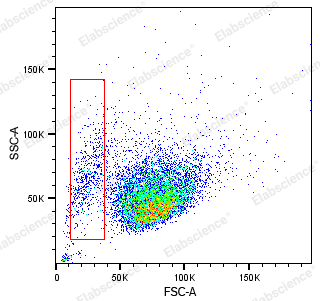
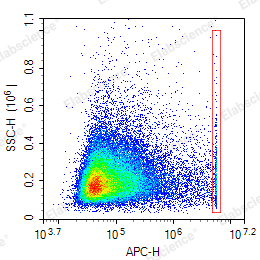
- A threshold that is too high may cause the apoptotic signal to be filtered out. Because when some cells undergo apoptosis, they shrink and FSC is smaller than normal cells (red box in Figure 3), and a threshold that is too high can lead to the inability to collect signals in this part.
- A threshold that is too small can result in most of the collected cells being cell fragments (Figure 4).
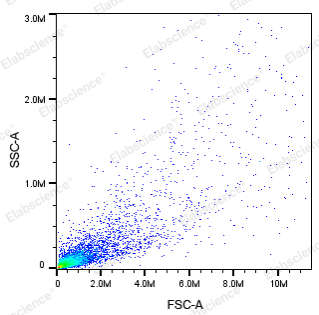
The voltage of each channel also needs to be set reasonably to ensure that the signal is within the acceptable range of the instrument and that the signal does not compress the line.
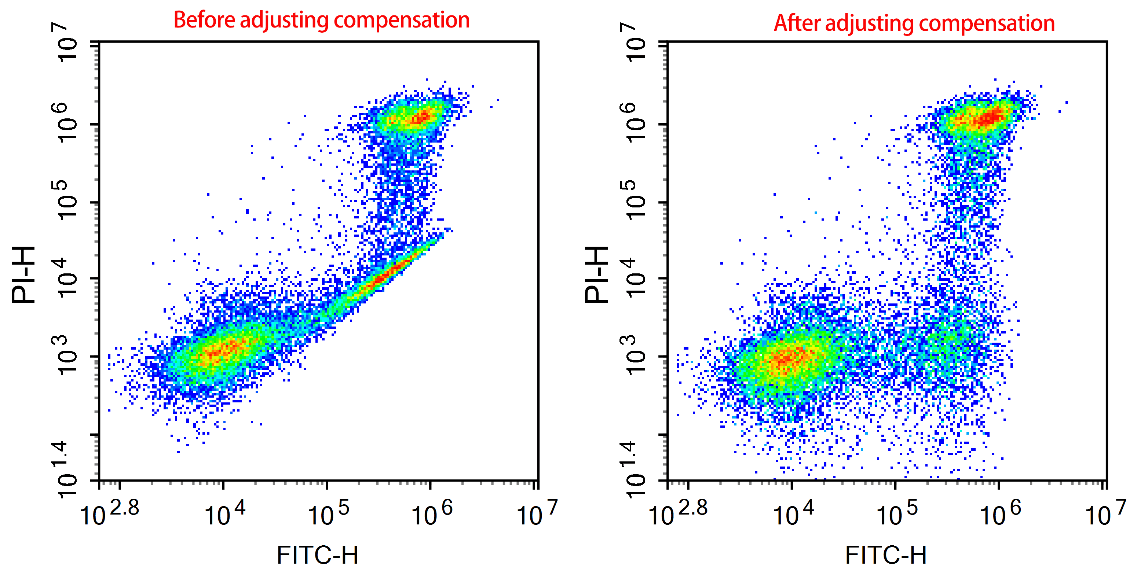
2) Compensation: Compensation adjustment is due to the phenomenon of spectral overlap between fluorescence, and it is necessary to remove the interference signal received in the target channel to ensure the credibility of the experimental results. The basis for compensating credibility is a good single positive control, so in the experimental design, it was mentioned that a single positive control must be done well to ensure that there is sufficient positive signal in the single positive tube.
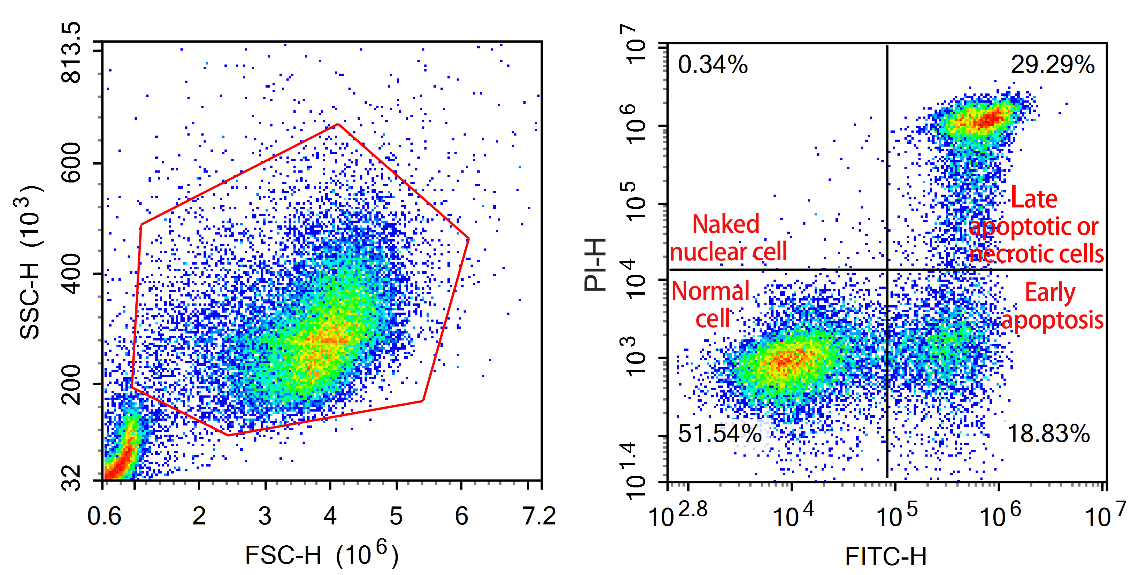
3) Gating: In the Annexin V experiment, cell grouping is usually more obvious, and setting a gate is not complicated - circle the target cell group on the FSC/SSC diagram, pay attention to the position of cell fragments, adjust the compensation, draw a cross gate, and fine tune the position of the cross gate in combination with the control group.
When circling the target cell population on the FSC/SSC diagram, it should be noted that some cells may undergo significant shrinkage due to apoptosis, and the FSC may be smaller than normal cells (left side of Figure 7). This part of the signal should also be circled to avoid loss of apoptotic signals, which may lead to biased experimental results.