|
Purpose |
Sample |
Antibody Collocation |
|
|
Adjust the voltage |
1 |
Blank |
|
|
Adjust compensation |
2 |
CD45-Elab Fluor® Red 780 |
|
|
3 |
CD3-FITC |
||
|
4 |
CD19-PE/Cyanine7 |
||
|
5 |
NK1.1-APC |
||
|
APC-FMO in combination with Isotype Control for auxiliary gating |
6 |
CD45-Elab Fluor® Red 780, CD3-FITC, CD19-PE/Cyanine7; Mouse IgG2a, κ Isotype Control-APC |
|
|
Full panel |
7 |
CD45-Elab Fluor® Red 780, CD3-FITC, CD19-PE/Cyanine7, NK1.1-APC |
|
Marker |
Fluorochrome |
Clone No. |
Cat. No. |
|
CD45 |
Elab Fluor® Red 780 |
30-F11 |
|
|
CD3 |
FITC |
17A2 |
|
|
CD19 |
PE/Cyanine7 |
1D3 |
|
|
NK1.1 |
APC |
PK136 |
|
|
Mouse IgG2a, κ Isotype Control |
APC |
C1.18.4 |
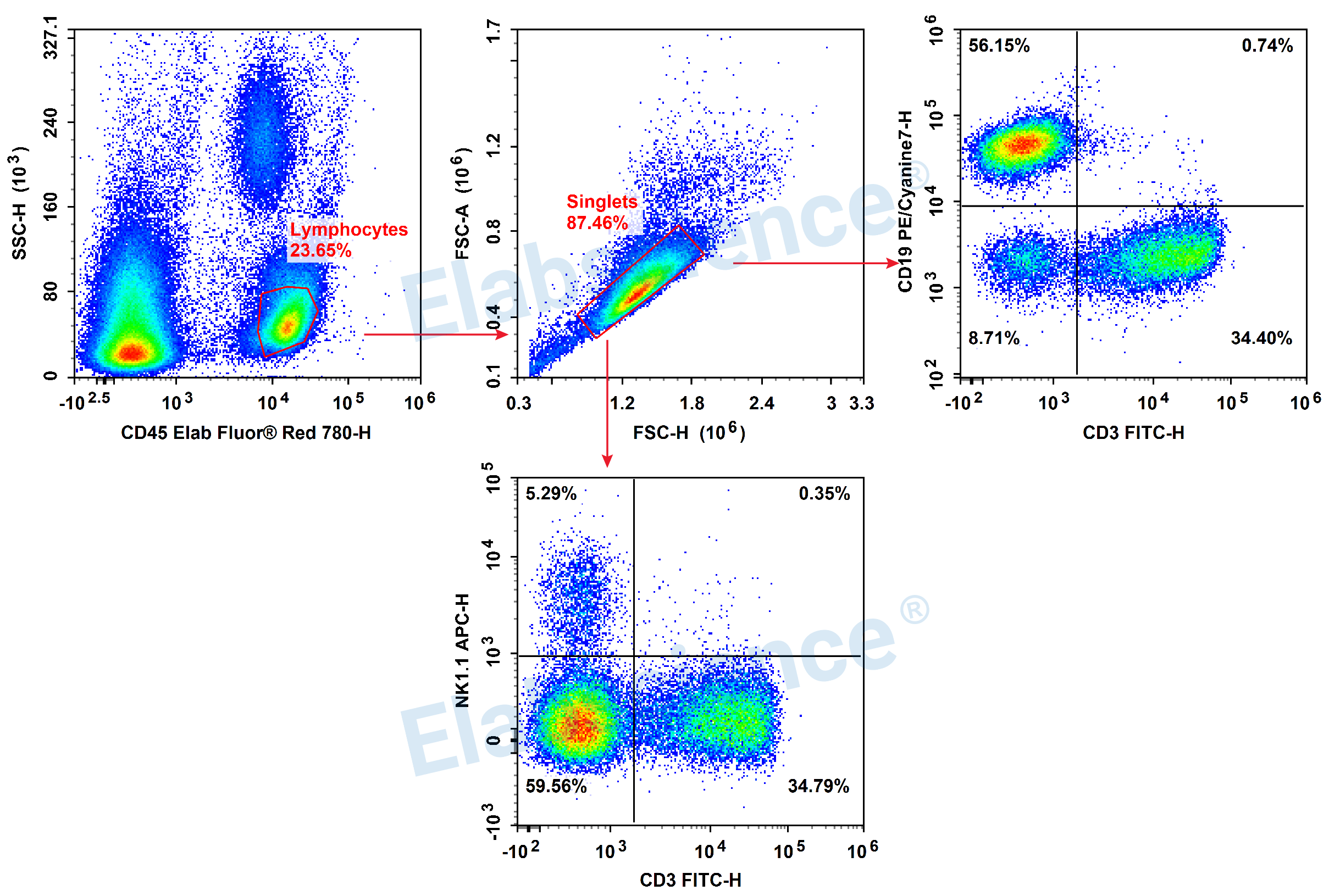
Tips:
1. Add CD45 indicators to peripheral blood samples, the lymphocyte populations can be gated directly through CD45 and SSC.
2. The CD3/CD4/CD8 cell populations are obvious, it can effectively distinguish between positive and negative cells even without Isotype Control.
3. The detection indicators of NK cells should be selected based on different mouse varieties, usually C57BL/6 mouse use NK1.1, and BALB/c mouse use CD49b (DX5). CD3-NK1.1+/CD3-CD49b+ is NK cells.
4. The key factor in this experiment is red blood cell lysis. Excessive or insufficient lysis of red blood cells can lead to unclear lymphocyte grouping.


