|
Purpose |
Sample |
Antibody Collocation |
|
|
Adjust the voltage |
1 |
Blank |
|
|
APC-FMO in combination with Isotype Control for auxiliary gating |
2 |
CD4-FITC, Rat IgG2a, κ Isotype Control-APC |
|
|
FITC-FMO in combination with Isotype Control for auxiliary gating |
3 |
CD8a-APC, Rat IgG2b, κ Isotype Control- FITC |
|
|
Full panel |
4 |
CD4-FITC, CD8a-APC |
|
Marker |
Fluorochrome |
Clone No. |
Cat. No. |
|
CD4 |
FITC |
GK1.5 |
|
|
CD8a |
APC |
53-6.7 |
|
|
Rat IgG2b, κ Isotype Control |
FITC |
LTF-2 |
|
|
Rat IgG2a, κ Isotype Control |
APC |
2A3 |
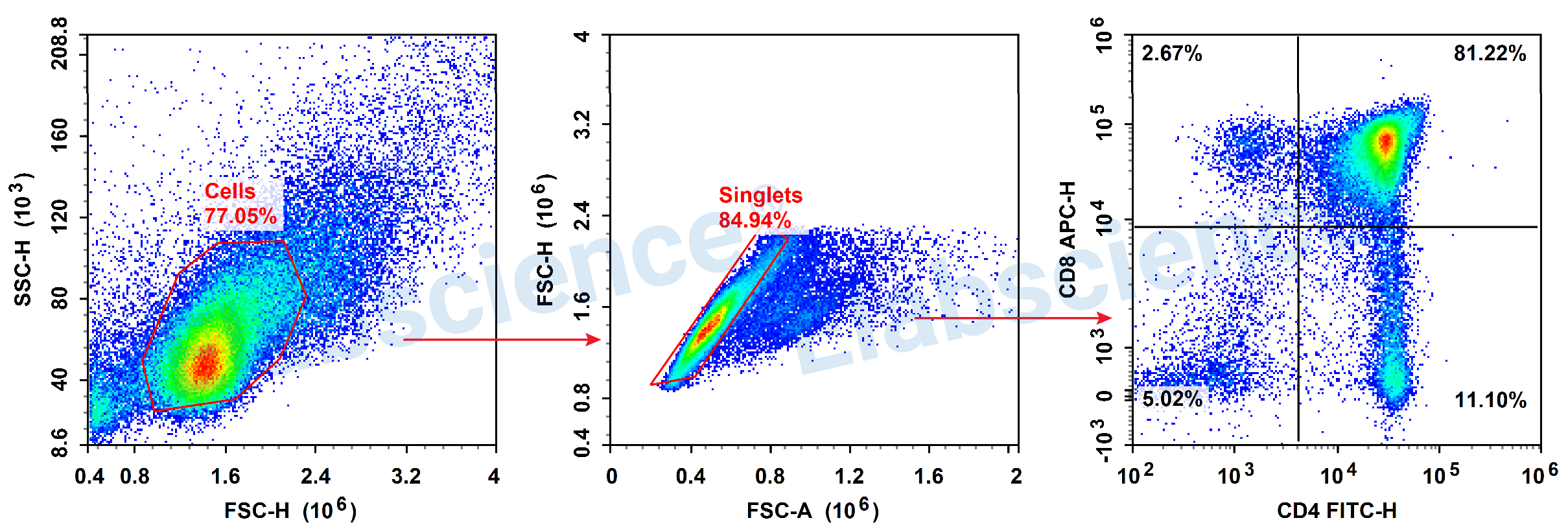
Tips:
1. According to the expression of CD4 and CD8, T cells in the thymus can be classified into double negative cells (DN cells: CD4-CD8-), double positive cells (DP cells: CD4+CD8+) and single positive cell (SP cell: CD4+CD8- or CD4-CD8+).
2. The majority of T cells in the thymus co-express CD4 and CD8. Choosing two non-interference fluorescent combinations, FITC and APC, during panel design can reduce the complexity of data analysis.
3. There is no interference between FITC and APC, so there is no need to set a single positive control compensation for this experiment.



