It is well-established that cytokines play a critical role in pathogen elimination and disease development. It is valuable to map the landscape of cytokines upon disease diagnosis and evaluation of the immune system function. However, the analysis of low-abundance cytokine is a challenge, as conventional methods often lack sufficient sensitivity. This article focuses on the limitation of traditional ELISA technology, and detail the advantages of high sensitivity ELISA.
Table of Contents
1. The Challenge of Detecting Low-abundance Cytokines in Serum and Plasma
2. Sensitivity Limit of ELISA Kits
3. Benefits for researchers using High-Sensitivity ELISA Kits
01 The Challenge of Detecting Low-abundance Cytokines in Serum and Plasma
The core challenge in detecting low-abundance cytokines using serum and plasma samples is the limitation of sensitivity. These proteins circulate at extremely low concentrations (often in the pg/mL or even fg/mL range) and are overwhelmed by high-abundance proteins (such as albumin and immunoglobulins), resulting in insufficient antigen capture in conventional methods[1]. Furthermore, matrix components present in serum and plasma, such as heterophilic antibodies and complement, can unspecifically bond to antigen-antibody complex, further elevating background noise[2]. Therefore, to achieve accurate detection, a high sensitivaty technological platform must overcome two hurdles. Firstly, it must possess a sufficiently low detection limit to "capture" the target molecules. Secondly, it must effectively overcome the interference from the complex matrix to "identify" the true signal.
02 Sensitivity Limit of ELISA Kits
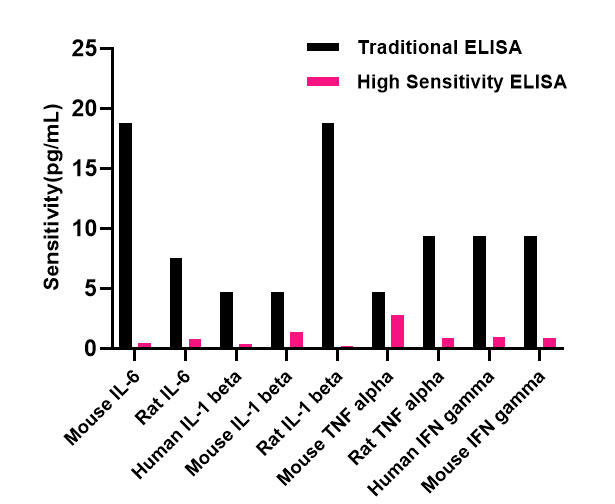
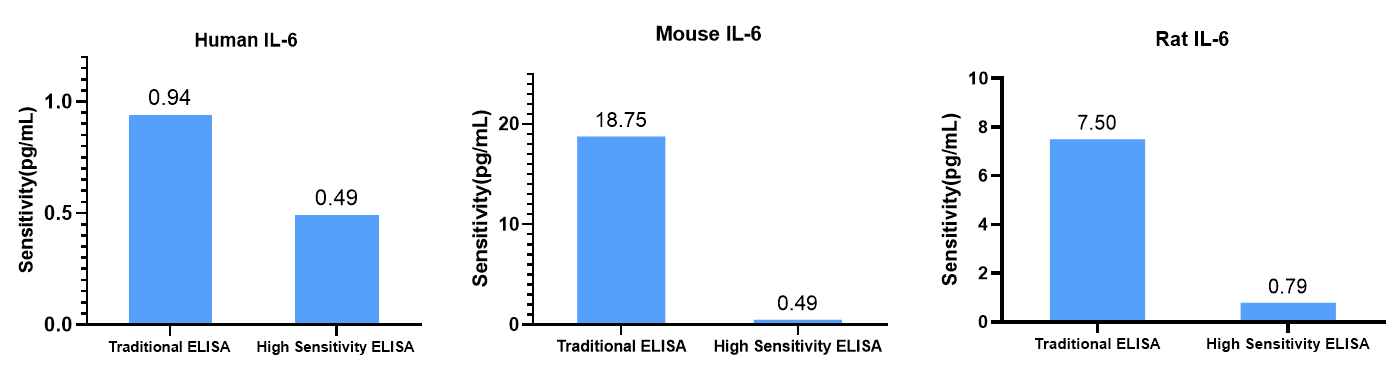
The difference between traditional ELISA and high sensitivity ELISA in cytokines analysis is their sensitivity limits, which directly determine the measurable concentration range. Typically, Traditional ELISA kits have a lower detection limit in the range of 1-10 pg/mL. For many constitutively expressed or highly expressed cytokines during inflammation, this level of sensitivity is sufficient. However, some cytokines may lower than 0.1 pg/mL in serum and plasma at physiological levels or during early disease stages,such as IL-6, IL-10, and IL-17A. Under this condition, conventional methods fail to detect analytes, resulting in data gaps or underestimation[3].
In contrast, high-sensitivity ELISA technology significantly enhances the detection limit to below 0.1 pg/mL, even reaching levels as low as 0.01 pg/mL, through optimized antibody pairs and more sensitive technical systems. This orders-of-magnitude improvement in sensitivity provides effective data support for research areas such as early disease monitoring.
Table.1 Comparison of Traditional ELISA and High Sensitivity ELISA Conditions
|
Item |
Traditional ELISA |
High Sensitivity ELISA |
|
Detection Sensitivity |
Moderate (typically 1-10 pg/mL) |
Exceptional (as low as 0.1 pg/mL or 0.01 pg/mL) |
|
Key Advantages |
Mature technology, high throughput |
Detects ultra-low concentrations, more comprehensive data, captures early-stage signals |
|
Suitable Applications |
Cell culture supernatants, highly expressed inflammatory cytokines |
Trace-level analysis in complex biological fluids (e.g., serum and plasma) |
|
Cost & Operation |
Lower cost, simple workflow |
Higher kit cost, simple workflow |
03 Benefits for researchers using High-Sensitivity ELISA Kits
3.1 Empowering Biomarker Discovery
Biomarker discovery relies on the accurate detection of trace-level molecules. High-Sensitivity Cytokine ELISA Kits enable reliable quantification of extremely low-abundance cytokines in complex samples, providing a superior solution for precise cytokine analysis. Compared to conventional methods, this technology allows researchers to identify subtle expression differences. Furthermore, when integrated into a multiplex cytokine assay platform, a single high-sensitivity cytokine ELISA kit can simultaneously quantify multiple targets, offering critical technical support for the discovery of promising novel diagnostic markers[4,5].
3.2 Cost-Effectiveness of High Sensitivity ELISA Kits in Research[6,7]
Decreased Experimental Repetition: Inconclusive results due to insufficient sensitivity waste precious samples, reagents and researchers time. High-Sensitivity ELISA kits minimizes the need for such repeated efforts.
Increased Data Value: High-Sensitivity ELISA kits significantly improve the depth and accuracy of research outcomes.
Accelerated Research Progress: Reliable detection results facilitate project progress, ultimately conserving valuable research time and human resources in the long term.
Selecting the most suitable detection tool is the fundamental step toward ensuring data reliability and research value. We are committed to supporting your cytokine research with our specialized products and services, providing critical support for your scientific endeavors.
Recommended Elabscience® High Sensitivity ELISA kits
Elabscience® High Sensitivity ELISA kits are a new series of kits that increase kit sensitivity by 2-10 times over Traditional ELISA kits to detect proteins at lowest Fg levels. Focusing on cytokine detection, the High Sensitivity ELISA kits are designed to solve the problem of low sample detection rates when testing samples with low target concentrations such as serum and plasma.
Core Advantages of Our Products:
● Compatible with Multiple Samples: Supports serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants, and various body fluids, providing flexibility for comprehensive cytokine analysis across diverse biological sources.
● Multi-Species and Multi-analytes Coverage: Includes human, mouse, and rat species, enabling broad cytokine profiling. The panel covers key targets such as IFN-γ, IL-1β (available as a dedicated il 1beta elisa kit), IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10.
● Higher sensitivity: increase kit sensitivity by 2-10 times over Traditional ELISA kits to detect proteins at lowest Fg levels.
● Superior Detection Performance: Excellent reproducibility with intra- and inter-assay CVs less than 10%.
● Worry-Free Service: One-on-one service with a 24-hour response.
Quick Overview of Popular Products
Table 2. High Sensitivity ELISA Kits for the Detection of Various Targets
|
Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Size |
|
E-HSEL-M0003 |
High Sensitivity Mouse IL-6 (Interleukin 6) ELISA Kit |
96 T/ 48 T/ 96 T × 5 |
|
E-HSEL-M0001 |
High Sensitivity Mouse IL-1β (Interleukin 1 Beta) ELISA Kit |
96 T/ 48 T/ 96 T × 5 |
|
E-HSEL-M0009 |
High Sensitivity Mouse TNF-α (Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
96 T/ 48 T/ 96 T × 5 |
|
E-HSEL-R0001 |
High Sensitivity Rat TNF-α (Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
96 T/ 48 T/ 96 T × 5 |
|
E-HSEL-R0002 |
High Sensitivity Rat IL-1β (Interleukin 1 Beta) ELISA Kit |
96 T/ 48 T/ 96 T × 5 |
|
E-HSEL-R0004 |
High Sensitivity Rat IL-6 (Interleukin 6) ELISA Kit |
96 T/ 48 T/ 96 T × 5 |
|
E-HSEL-H0003 |
High Sensitivity Human IL-6 (Interleukin 6) ELISA Kit |
96 T/ 48 T/ 96 T × 5 |
|
E-HSEL-H0007 |
High Sensitivity Human IFN-γ (Interferon Gamma) ELISA Kit |
96 T/ 48 T/ 96 T × 5 |
|
E-HSEL-H0001 |
High Sensitivity Human IL-1β (Interleukin 1 Beta) ELISA Kit |
96 T/ 48 T/ 96 T × 5 |
References:
[1] Rissin, D. M., et al. (2010). Single-molecule enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detects serum proteins at sub-femtomolar concentrations. Nature Biotechnology, 28(6), 595–599.
[2] Bolstad, N., Warren, D. J., & Nustad, K. (2013). Heterophilic antibody interference in immunometric assays. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 27(5), 647-661.
[3] de Jager, W., & Rijkers, G. T. (2006). Solid-phase and bead-based cytokine immunoassay: a comparison. Methods, 38(4), 294-303.
[4] Leng, S. X., et al. (2008). ELISA and multiplex technologies for cytokine measurement in inflammation and aging research. The Journals of Gerontology: Series A, 63(8), 879-884.
[5] Rissin, D. M., et al. (2010). Single-molecule enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detects serum proteins at sub-femtomolar concentrations. Nature Biotechnology, 28(6), 595-599.
[6] Zhang, Y., Chen, K., Wang, Z., Liu, J., Li, Y., Wang, B., Li, J., & Liu, X. (2024). Eliminating radioresistance with a magnetic ion-generator by simultaneously augmenting DNA damage and diminishing immunosuppression. Advanced Materials, 2406378.
[7] Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., Chen, K., Wang, B., Liu, J., Li, J., & Liu, X. (2024). Multifunctional nanotheranostic agent for NIR-II fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging-guided cancer therapy. ACS Nano, *18*(19), 12385–12400.



